Food Recognition
Food recognition is the process of identifying and categorizing different types of food in images or videos.
Papers and Code
Mam-App: A Novel Parameter-Efficient Mamba Model for Apple Leaf Disease Classification
Jan 29, 2026The rapid growth of the global population, alongside exponential technological advancement, has intensified the demand for food production. Meeting this demand depends not only on increasing agricultural yield but also on minimizing food loss caused by crop diseases. Diseases account for a substantial portion of apple production losses, despite apples being among the most widely produced and nutritionally valuable fruits worldwide. Previous studies have employed machine learning techniques for feature extraction and early diagnosis of apple leaf diseases, and more recently, deep learning-based models have shown remarkable performance in disease recognition. However, most state-of-the-art deep learning models are highly parameter-intensive, resulting in increased training and inference time. Although lightweight models are more suitable for user-friendly and resource-constrained applications, they often suffer from performance degradation. To address the trade-off between efficiency and performance, we propose Mam-App, a parameter-efficient Mamba-based model for feature extraction and leaf disease classification. The proposed approach achieves competitive state-of-the-art performance on the PlantVillage Apple Leaf Disease dataset, attaining 99.58% accuracy, 99.30% precision, 99.14% recall, and a 99.22% F1-score, while using only 0.051M parameters. This extremely low parameter count makes the model suitable for deployment on drones, mobile devices, and other low-resource platforms. To demonstrate the robustness and generalizability of the proposed model, we further evaluate it on the PlantVillage Corn Leaf Disease and Potato Leaf Disease datasets. The model achieves 99.48%, 99.20%, 99.34%, and 99.27% accuracy, precision, recall, and F1-score on the corn dataset and 98.46%, 98.91%, 95.39%, and 97.01% on the potato dataset, respectively.
Deep Learning-Based Image Recognition for Soft-Shell Shrimp Classification
Jan 06, 2026With the integration of information technology into aquaculture, production has become more stable and continues to grow annually. As consumer demand for high-quality aquatic products rises, freshness and appearance integrity are key concerns. In shrimp-based processed foods, freshness declines rapidly post-harvest, and soft-shell shrimp often suffer from head-body separation after cooking or freezing, affecting product appearance and consumer perception. To address these issues, this study leverages deep learning-based image recognition for automated classification of white shrimp immediately after harvest. A convolutional neural network (CNN) model replaces manual sorting, enhancing classification accuracy, efficiency, and consistency. By reducing processing time, this technology helps maintain freshness and ensures that shrimp transportation businesses meet customer demands more effectively.
SignIT: A Comprehensive Dataset and Multimodal Analysis for Italian Sign Language Recognition
Dec 16, 2025In this work we present SignIT, a new dataset to study the task of Italian Sign Language (LIS) recognition. The dataset is composed of 644 videos covering 3.33 hours. We manually annotated videos considering a taxonomy of 94 distinct sign classes belonging to 5 macro-categories: Animals, Food, Colors, Emotions and Family. We also extracted 2D keypoints related to the hands, face and body of the users. With the dataset, we propose a benchmark for the sign recognition task, adopting several state-of-the-art models showing how temporal information, 2D keypoints and RGB frames can be influence the performance of these models. Results show the limitations of these models on this challenging LIS dataset. We release data and annotations at the following link: https://fpv-iplab.github.io/SignIT/.
Evaluating Gemini LLM in Food Image-Based Recipe and Nutrition Description with EfficientNet-B4 Visual Backbone
Nov 11, 2025



The proliferation of digital food applications necessitates robust methods for automated nutritional analysis and culinary guidance. This paper presents a comprehensive comparative evaluation of a decoupled, multimodal pipeline for food recognition. We evaluate a system integrating a specialized visual backbone (EfficientNet-B4) with a powerful generative large language model (Google's Gemini LLM). The core objective is to evaluate the trade-offs between visual classification accuracy, model efficiency, and the quality of generative output (nutritional data and recipes). We benchmark this pipeline against alternative vision backbones (VGG-16, ResNet-50, YOLOv8) and a lightweight LLM (Gemma). We introduce a formalization for "Semantic Error Propagation" (SEP) to analyze how classification inaccuracies from the visual module cascade into the generative output. Our analysis is grounded in a new Custom Chinese Food Dataset (CCFD) developed to address cultural bias in public datasets. Experimental results demonstrate that while EfficientNet-B4 (89.0\% Top-1 Acc.) provides the best balance of accuracy and efficiency, and Gemini (9.2/10 Factual Accuracy) provides superior generative quality, the system's overall utility is fundamentally bottlenecked by the visual front-end's perceptive accuracy. We conduct a detailed per-class analysis, identifying high semantic similarity as the most critical failure mode.
What's on Your Plate? Inferring Chinese Cuisine Intake from Wearable IMUs
Nov 07, 2025Accurate food intake detection is vital for dietary monitoring and chronic disease prevention. Traditional self-report methods are prone to recall bias, while camera-based approaches raise concerns about privacy. Furthermore, existing wearable-based methods primarily focus on a limited number of food types, such as hamburgers and pizza, failing to address the vast diversity of Chinese cuisine. To bridge this gap, we propose CuisineSense, a system that classifies Chinese food types by integrating hand motion cues from a smartwatch with head dynamics from smart glasses. To filter out irrelevant daily activities, we design a two-stage detection pipeline. The first stage identifies eating states by distinguishing characteristic temporal patterns from non-eating behaviors. The second stage then conducts fine-grained food type recognition based on the motions captured during food intake. To evaluate CuisineSense, we construct a dataset comprising 27.5 hours of IMU recordings across 11 food categories and 10 participants. Experiments demonstrate that CuisineSense achieves high accuracy in both eating state detection and food classification, offering a practical solution for unobtrusive, wearable-based dietary monitoring.The system code is publicly available at https://github.com/joeeeeyin/CuisineSense.git.
MARC: Multimodal and Multi-Task Agentic Retrieval-Augmented Generation for Cold-Start Recommender System
Nov 15, 2025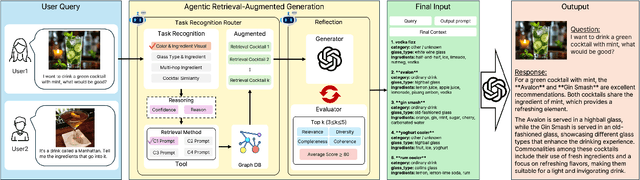
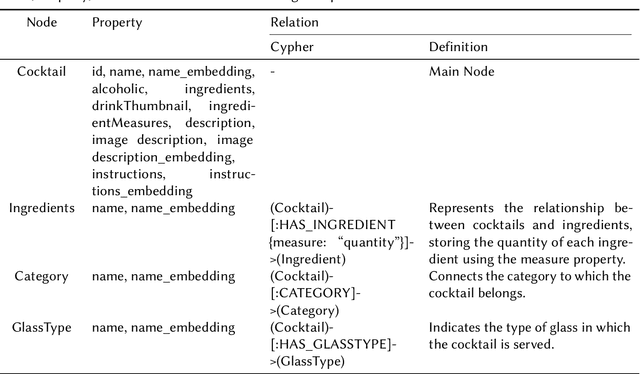
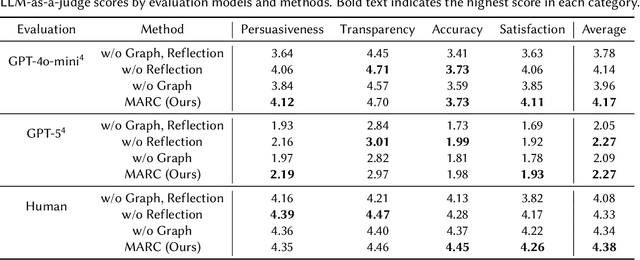
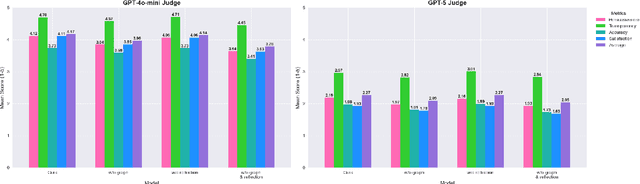
Recommender systems (RS) are currently being studied to mitigate limitations during cold-start conditions by leveraging modality information or introducing Agent concepts based on the exceptional reasoning capabilities of Large Language Models (LLMs). Meanwhile, food and beverage recommender systems have traditionally used knowledge graph and ontology concepts due to the domain's unique data attributes and relationship characteristics. On this background, we propose MARC, a multimodal and multi-task cocktail recommender system based on Agentic Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) utilizing graph database under cold-start conditions. The proposed system generates high-quality, contextually appropriate answers through two core processes: a task recognition router and a reflection process. The graph database was constructed by processing cocktail data from Kaggle, and its effectiveness was evaluated using 200 manually crafted questions. The evaluation used both LLM-as-a-judge and human evaluation to demonstrate that answers generated via the graph database outperformed those from a simple vector database in terms of quality. The code is available at https://github.com/diddbwls/cocktail_rec_agentrag
SalientFusion: Context-Aware Compositional Zero-Shot Food Recognition
Sep 04, 2025Food recognition has gained significant attention, but the rapid emergence of new dishes requires methods for recognizing unseen food categories, motivating Zero-Shot Food Learning (ZSFL). We propose the task of Compositional Zero-Shot Food Recognition (CZSFR), where cuisines and ingredients naturally align with attributes and objects in Compositional Zero-Shot learning (CZSL). However, CZSFR faces three challenges: (1) Redundant background information distracts models from learning meaningful food features, (2) Role confusion between staple and side dishes leads to misclassification, and (3) Semantic bias in a single attribute can lead to confusion of understanding. Therefore, we propose SalientFusion, a context-aware CZSFR method with two components: SalientFormer, which removes background redundancy and uses depth features to resolve role confusion; DebiasAT, which reduces the semantic bias by aligning prompts with visual features. Using our proposed benchmarks, CZSFood-90 and CZSFood-164, we show that SalientFusion achieves state-of-the-art results on these benchmarks and the most popular general datasets for the general CZSL. The code is avaliable at https://github.com/Jiajun-RUC/SalientFusion.
STA-Net: A Decoupled Shape and Texture Attention Network for Lightweight Plant Disease Classification
Sep 03, 2025Responding to rising global food security needs, precision agriculture and deep learning-based plant disease diagnosis have become crucial. Yet, deploying high-precision models on edge devices is challenging. Most lightweight networks use attention mechanisms designed for generic object recognition, which poorly capture subtle pathological features like irregular lesion shapes and complex textures. To overcome this, we propose a twofold solution: first, using a training-free neural architecture search method (DeepMAD) to create an efficient network backbone for edge devices; second, introducing the Shape-Texture Attention Module (STAM). STAM splits attention into two branches -- one using deformable convolutions (DCNv4) for shape awareness and the other using a Gabor filter bank for texture awareness. On the public CCMT plant disease dataset, our STA-Net model (with 401K parameters and 51.1M FLOPs) reached 89.00% accuracy and an F1 score of 88.96%. Ablation studies confirm STAM significantly improves performance over baseline and standard attention models. Integrating domain knowledge via decoupled attention thus presents a promising path for edge-deployed precision agriculture AI. The source code is available at https://github.com/RzMY/STA-Net.
COBRA: Multimodal Sensing Deep Learning Framework for Remote Chronic Obesity Management via Wrist-Worn Activity Monitoring
Sep 04, 2025Chronic obesity management requires continuous monitoring of energy balance behaviors, yet traditional self-reported methods suffer from significant underreporting and recall bias, and difficulty in integration with modern digital health systems. This study presents COBRA (Chronic Obesity Behavioral Recognition Architecture), a novel deep learning framework for objective behavioral monitoring using wrist-worn multimodal sensors. COBRA integrates a hybrid D-Net architecture combining U-Net spatial modeling, multi-head self-attention mechanisms, and BiLSTM temporal processing to classify daily activities into four obesity-relevant categories: Food Intake, Physical Activity, Sedentary Behavior, and Daily Living. Validated on the WISDM-Smart dataset with 51 subjects performing 18 activities, COBRA's optimal preprocessing strategy combines spectral-temporal feature extraction, achieving high performance across multiple architectures. D-Net demonstrates 96.86% overall accuracy with category-specific F1-scores of 98.55% (Physical Activity), 95.53% (Food Intake), 94.63% (Sedentary Behavior), and 98.68% (Daily Living), outperforming state-of-the-art baselines by 1.18% in accuracy. The framework shows robust generalizability with low demographic variance (<3%), enabling scalable deployment for personalized obesity interventions and continuous lifestyle monitoring.
An Explorative Analysis of SVM Classifier and ResNet50 Architecture on African Food Classification
May 20, 2025Food recognition systems has advanced significantly for Western cuisines, yet its application to African foods remains underexplored. This study addresses this gap by evaluating both deep learning and traditional machine learning methods for African food classification. We compared the performance of a fine-tuned ResNet50 model with a Support Vector Machine (SVM) classifier. The dataset comprises 1,658 images across six selected food categories that are known in Africa. To assess model effectiveness, we utilize five key evaluation metrics: Confusion matrix, F1-score, accuracy, recall and precision. Our findings offer valuable insights into the strengths and limitations of both approaches, contributing to the advancement of food recognition for African cuisines.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge